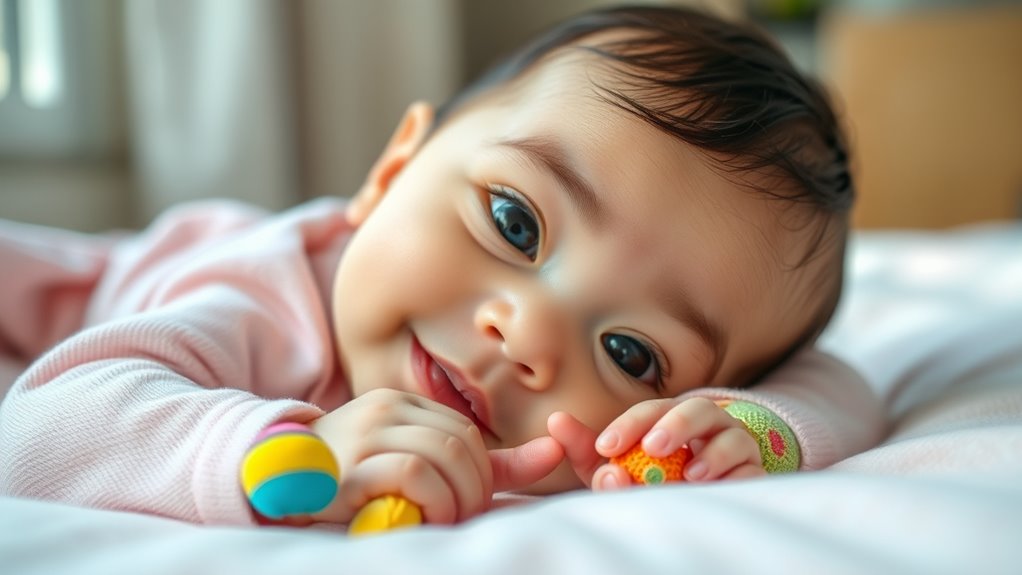
To recognize early signs of emotional well-being in your infant, observe their responsiveness, curiosity, and comfort in social interactions. A happy, secure baby shows regular curiosity, seeks comfort when needed, and responds positively to caregiver engagement. Consistent, nurturing interactions help build attachment security and emotional resilience. If your baby displays joy, trust, and adaptability, these are good indicators of health. Keep exploring further to learn how to support your little one’s emotional growth from the start.
Key Takeaways
- Happy, alert, and responsive behavior indicates healthy emotional well-being in infants.
- Consistent eye contact and seeking comfort reflect secure attachment and emotional stability.
- Regular social interactions and joyful responses signal positive emotional development.
- Absence of excessive crying or withdrawal suggests balanced emotional regulation.
- Smooth adaptation to routines and environments shows resilience and secure attachment.
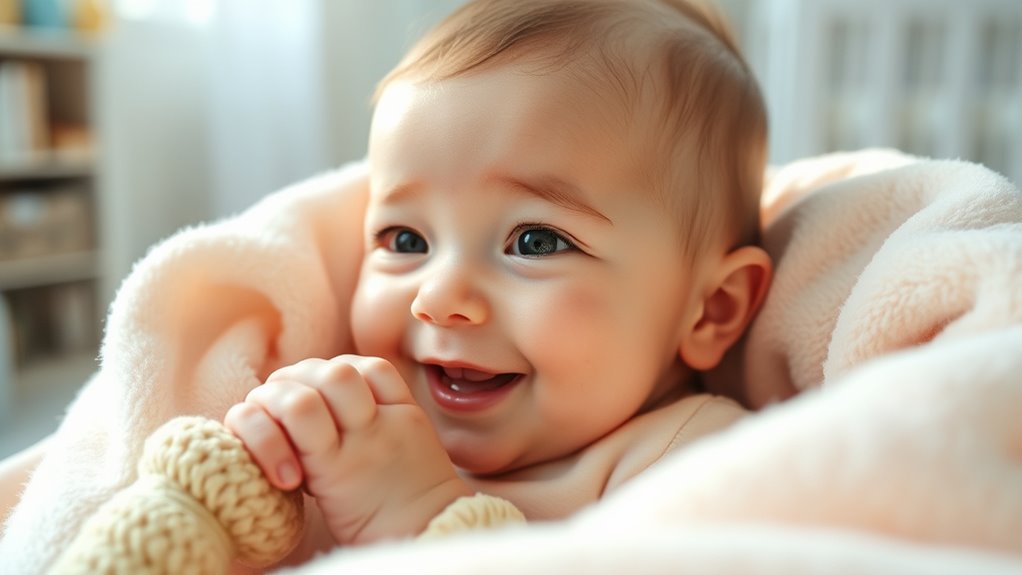

Infant mental health is the foundation for a child’s overall well-being and development, yet it often remains overlooked. As a caregiver, your interactions play a crucial role in shaping your baby’s emotional health from the very start. One of the key aspects of early mental health is attachment security, which develops through consistent, responsive caregiver interactions. When you respond promptly and sensitively to your infant’s needs—whether they’re hungry, uncomfortable, or seeking comfort—you help build a strong, secure bond. This bond reassures your baby that they can trust you, creating a safe environment where they feel confident to explore and learn.
Secure attachment isn’t just about meeting basic needs; it’s about engaging in meaningful, nurturing interactions that foster emotional regulation. When your baby cries, and you respond with warmth and understanding, you signal that their feelings are valid and manageable. This consistent responsiveness helps your child develop a sense of trust and safety, laying the groundwork for healthy emotional development. Conversely, inconsistent or neglectful interactions can undermine attachment security, leading to potential challenges in emotional regulation and social relationships later in life.
Responsive, nurturing interactions foster trust and emotional regulation, laying the foundation for healthy development and lifelong resilience.
You can promote attachment security by paying close attention to your baby’s cues. Notice how they express their needs through different sounds, gestures, or facial expressions, and respond appropriately. For example, if your infant reaches out or makes eye contact, it’s a sign they’re seeking connection. When you meet those signals with gentle touch, eye contact, and soothing words, you reinforce their sense of security. This helps your baby learn that their feelings are understood and that they can rely on you, which is fundamental for emotional resilience. Developing secure attachment early on can influence their capacity for emotional regulation and social skills as they grow.
Remember, caregiver interactions aren’t just about physical caregiving but also about emotional availability. Your presence, tone of voice, and facial expressions all communicate safety and love. Even simple routines like reading a book together, singing, or cuddling can strengthen your bond and support healthy mental development. These interactions are opportunities to nurture attachment security, which influences your child’s ability to regulate emotions, handle stress, and develop social skills later on.
In essence, your consistent, sensitive responses create a foundation for your infant’s mental health. Recognizing the importance of attachment security and prioritizing positive caregiver interactions can help your child grow into a confident, emotionally healthy individual. Your role in their early years is essential—each moment of connection shapes their future emotional well-being and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Parents Support Infant Emotional Development Daily?
You can support your infant’s emotional development daily through playful interactions, which help build trust and joy. Keep consistent routines to provide a sense of security and predictability. Respond promptly to their cues, offering comfort and encouragement. Engaging in eye contact, smiling, and gentle touch strengthens your bond. These simple, daily actions nurture your baby’s emotional well-being, fostering confidence and healthy emotional growth over time.
What Are Common Signs of Emotional Distress in Infants?
You might notice emotional distress in infants through subtle emotional cues like increased crying, fussiness, or withdrawal. Behavioral indicators include difficulty calming down, changes in sleep or feeding patterns, or excessive clinginess. These signs suggest your baby may be overwhelmed or unsettled. Pay close attention to these cues, respond with comfort and patience, and consult a healthcare professional if concerns persist, ensuring your little one feels safe and supported.
When Should I Seek Professional Help for My Infant’s Emotional Health?
You should seek professional help as soon as you notice your infant struggles to reach key emotional milestones or shows persistent signs of distress. Early intervention can prevent issues from becoming overwhelming, ensuring your baby’s emotional well-being. Trust your instincts; if something feels off or your baby’s reactions seem unusual, don’t wait. Prompt support can make a world of difference in nurturing healthy emotional development from the start.
How Does Infant Mental Health Impact Later Development?
Your infant’s mental health influences their attachment security and emotional resilience, shaping future relationships and stress management. When they develop strong emotional skills early, they’re more likely to form secure attachments, which foster confidence and social competence later on. By nurturing their emotional well-being now, you help build a solid foundation for healthy development, leading to better outcomes in academics, relationships, and overall mental health as they grow.
Are There Specific Activities That Promote Emotional Well-Being in Infants?
You can promote emotional well-being in infants through simple activities like sensory play and bonding activities. Sensory play, such as exploring different textures or listening to soothing sounds, helps your baby develop trust and regulate emotions. Bonding activities like cuddling, singing, or eye contact strengthen your connection, providing a sense of security. Regularly engaging in these activities nurtures your infant’s emotional health and builds a solid foundation for future development.
Conclusion
Just as the first notes of a symphony set the tone for the entire piece, recognizing early signs of your infant’s emotional well-being shapes a lifetime of healthy development. By paying attention now, you nurture a foundation as sturdy as a oak tree’s roots—unseen but essential. Remember, your gentle care and awareness are the guiding stars that light the path toward a bright, resilient future for your little one, just like a lighthouse guides ships home.