The fourth trimester, lasting about 12 weeks after childbirth, is a crucial time for your physical recovery and emotional adjustment. You’ll experience hormonal shifts, uterine contractions, and ongoing tissue healing, while facing mood swings and bonding challenges. Cultural practices like rest, special diets, and community support often help you heal emotionally and physically. If you’d like to explore how to navigate this period with confidence, there’s much more to discover about its medical and cultural aspects.
Key Takeaways
- The fourth trimester is the first 12 weeks postpartum focused on physical recovery and emotional adjustment.
- It involves hormonal shifts, uterine involution, healing, and breastfeeding support.
- Cultural practices like confinement, herbal remedies, and community support aid recovery and bonding.
- Emotional fluctuations are common; support networks and self-care help prevent postpartum depression.
- Regular medical check-ups monitor healing, address complications, and promote overall well-being during this transitional phase.
Understanding the Fourth Trimester: Definition and Duration

The fourth trimester, often called the “postpartum period,” begins immediately after your baby is born and lasts about 12 weeks. During this time, your body undergoes rapid changes as it recovers from childbirth and adjusts to caring for your newborn. It’s a transitional phase where hormonal shifts, uterine contraction, and tissue healing happen simultaneously. You’ll likely notice physical sensations like bleeding, soreness, and fatigue. This period isn’t just about physical recovery; it’s also about emotional adjustments as you bond with your baby. While the duration is roughly 12 weeks, everyone’s experience varies. Recognizing this phase helps you understand that your body and emotions are both changing, and that this time is essential for laying the foundation for postpartum healing and adjustment. Paying attention to physical recovery can help ensure a smoother transition through this important phase.
Physical Changes and Recovery for Mothers

After your baby arrives, your body starts working hard to heal and adapt. You’ll notice bleeding, called lochia, which gradually decreases over weeks. Your uterus shrinks back to its pre-pregnancy size, a process called involution, often causing some cramping. You might experience soreness or discomfort around your perineum or cesarean incision, which improves with time. Hormonal shifts can cause fatigue, hot flashes, or night sweats. Your breasts may become swollen and tender as they prepare for breastfeeding, and you might have to manage engorgement or soreness. Recovery also involves your pelvic floor muscles, which may feel weak or stretched. Rest, proper hydration, and gentle activity help your body heal faster. Monitoring newborn bowel movements can be helpful during recovery, as changes in stool patterns may indicate health issues. Remember, everyone’s recovery timeline differs, so listen to your body and seek support when needed.
Emotional and Psychological Adjustments After Birth

After birth, you might notice your emotions fluctuate more than you expected, making it hard to stay balanced. Bonding with your baby can also bring unexpected challenges that catch you off guard. Having emotional support strategies in place can help you navigate these feelings and strengthen your connection. Understanding the emotional and psychological changes during this period can empower you to cope more effectively.
Postpartum Mood Fluctuations
Have you noticed how your emotions can swing unexpectedly during the weeks following childbirth? These postpartum mood fluctuations are common and can range from joy to irritability or sadness. You might feel overwhelmed even when things seem manageable. Hormonal shifts, sleep deprivation, and physical recovery all contribute to these changes. It’s important to recognize that these feelings are normal and temporary. Additionally, understanding hormonal influences on mood can help you better manage emotional responses during this period.
Consider these factors:
- Hormonal fluctuations affecting mood stability
- Fatigue impacting emotional resilience
- Adjustment to new responsibilities
- External pressures from family and society
- Personal history influencing reactions
Bonding Challenges Emerge
Bonding challenges often surface as new parents navigate the emotional and psychological adjustments that come with caring for a newborn. You might feel overwhelmed, unsure, or disconnected during this time. These feelings are common and can stem from sleep deprivation, hormonal shifts, or the pressure to bond instantly. Recognizing this is vital—you’re not alone. To visualize, consider this table:
| Emotional State | Common Experience |
|---|---|
| Anxiety | Worrying about doing everything right |
| Exhaustion | Constant fatigue and sleep loss |
| Disconnection | Feeling distant from your baby |
Understanding these challenges helps you normalize your feelings and prepare for the adjustment period ahead. Remember, bonding takes time, patience, and support. Building a bonding process takes patience and intentional effort, which can ease feelings of disconnection over time.
Emotional Support Strategies
Maneuvering the emotional and psychological changes that come with caring for a newborn can be challenging, but implementing effective support strategies can make a significant difference. Recognizing your feelings, seeking help, and practicing self-care are key. Don’t hesitate to talk openly with your partner, friends, or a mental health professional about your emotions. Taking time for yourself, even in small ways, helps maintain balance. Remember, postpartum moods are normal, but persistent feelings of sadness or anxiety deserve attention. Building a support network can provide comfort and guidance during this shift. Utilizing emotional support strategies such as mindfulness and relaxation techniques can further aid in managing stress.
Common Postpartum Health Concerns and Management

After giving birth, you might notice bleeding and discharge as your body heals, which is normal but important to monitor. You may also experience mood swings or emotional shifts that can surprise you. Understanding these common concerns helps you manage them effectively and seek help if needed. Recognizing the emotional aspects of good grief can support your mental health during this transition.
Postpartum Bleeding and Discharge
Have you noticed bleeding or discharge after giving birth? It’s normal for your body to shed the lining of your uterus, resulting in postpartum bleeding called lochia. This bleeding can last for several weeks and change in color and heaviness over time. You might notice bright red blood initially, gradually turning pink or brown. To manage this, use maternity pads and change them frequently. Keep an eye out for excessive bleeding, large clots, or foul odor, which could signal infection or other issues. Staying hydrated and resting helps your body heal. Remember, bleeding patterns vary, but if you experience heavy bleeding or severe pain, contact your healthcare provider promptly. Automation in healthcare and other innovations are advancing postpartum care options.
Emotional and Mood Changes
Emotional and mood changes are common during the postpartum period, and many new mothers experience a wide range of feelings as their bodies adjust. You might feel joy one moment and sadness the next, which is normal. Hormonal shifts, sleep deprivation, and physical recovery influence these emotions. Recognizing these feelings helps you manage them better. Sometimes, these changes can lead to postpartum depression or anxiety, requiring professional support. Understanding your emotional state is essential for your well-being and bond with your baby. Use this table to understand different emotions and their meanings:
| Emotion | Common Causes | Suggested Management |
|---|---|---|
| Happiness | Bonding, achievement | Celebrate milestones |
| Sadness | Hormonal fluctuations | Rest, seek support |
| Anxiety | New responsibilities | Practice relaxation techniques |
| Overwhelm | Sleep deprivation, physical recovery | Ask for help, prioritize self-care |
Additionally, being aware of the importance of seeking support can significantly improve your postpartum experience.
The Role of Postpartum Care and Medical Follow-Up

Postpartum care and medical follow-up are essential components of the fourth trimester, ensuring both your recovery and your baby’s well-being. Regular check-ups help identify issues like infections, bleeding, or complications early on. They also monitor your mental health, addressing concerns like postpartum depression. During these visits, your healthcare provider assesses your physical healing and provides guidance on breastfeeding, sleep, and self-care. Staying proactive with follow-up appointments helps you recover comfortably and reduces risks. Being aware of retirement planning options can also help ensure your financial stability during this important life stage.
Cultural Practices Supporting New Mothers Worldwide
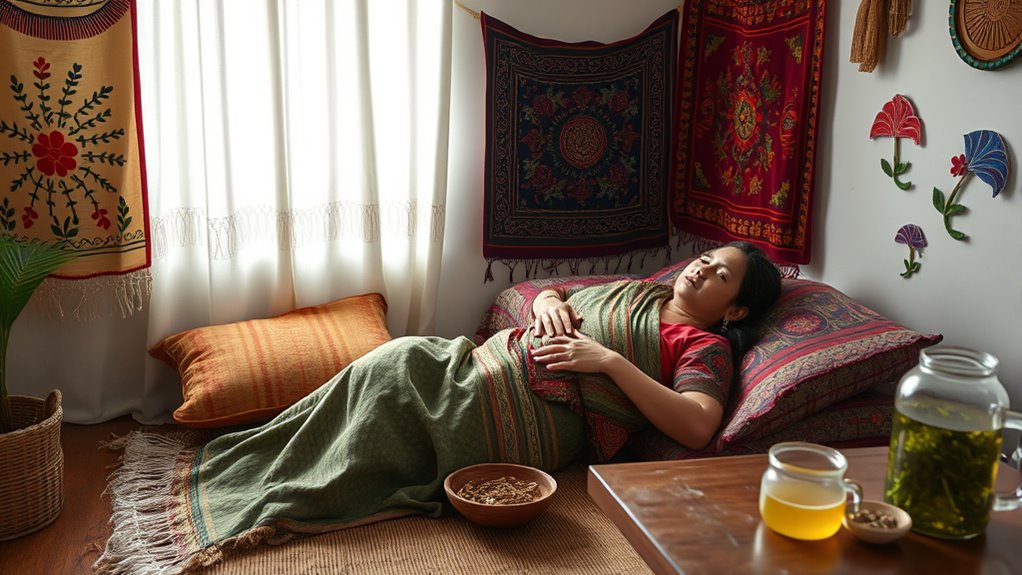

Across cultures, traditional practices play a pivotal role in supporting new mothers during the postpartum period. Many societies have specific routines to help women recover physically and emotionally. For example, in some Asian cultures, new mothers are encouraged to rest extensively, avoid cold foods, and stay indoors to promote healing. In parts of Africa, postpartum confinement includes community support, nutrition, and rest to restore strength. Latin American communities often practice “la cuarentena,” a period of rest and care where family members assist with household tasks. These practices reinforce the importance of community, rest, and proper nutrition, helping women regain energy and confidence. By embracing such customs, you can feel supported and connected, easing the transition into new motherhood.
Traditional Rituals and Their Significance in Postpartum Care

Traditional rituals surrounding childbirth serve an essential role in guiding new mothers through their recovery by reinforcing cultural values and promoting well-being. These rituals provide a sense of continuity, community support, and comfort during a vulnerable time. They often include specific practices like herbal baths, dietary restrictions, or dedicated rest periods, all aimed at restoring strength and bonding with the baby. Such customs can vary widely across cultures but share a common goal of nurturing both body and mind. Engaging in these traditions helps you feel connected to your heritage and provides emotional reassurance. Furthermore, they emphasize the importance of self-care and family involvement.
- Herbal remedies for healing
- Postpartum confinement practices
- Rituals for calming and bonding
- Special foods for recovery
- Community support ceremonies
Nutritional and Lifestyle Recommendations During the Fourth Trimester

During the fourth trimester, focusing on a nutrient-rich diet helps support your recovery and milk production. Prioritizing rest and self-care is essential for your physical and emotional well-being. By making small adjustments, you can boost your energy and feel more balanced as you recover.
Nutrient-Rich Diet Tips
Eating a nutrient-rich diet in the fourth trimester is essential for your recovery and overall well-being. Focus on incorporating a variety of whole foods that support healing, energy, and milk production if you’re breastfeeding. Prioritize lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Staying hydrated is equally important, so drink plenty of water throughout the day. Consider adding iron-rich foods to replenish stores and calcium for bone health. Avoid processed foods and excess sugar to minimize inflammation and fatigue. Planning balanced meals can help you meet your nutritional needs and boost your mood. Remember, nourishing your body helps you recover faster and feel more energized during this vital postpartum period.
- Include plenty of leafy greens and colorful vegetables
- Incorporate lean meats, fish, or plant-based proteins
- Snack on nuts, seeds, and yogurt for added nutrients
- Limit caffeine and sugary drinks
- Opt for whole grains over refined carbs
Rest and Self-Care
Prioritizing rest and self-care is essential for your recovery and well-being in the fourth trimester. Giving yourself permission to slow down helps your body heal and stabilizes your emotions. Focus on adequate sleep, gentle activity, and nourishing meals. Remember, asking for help is okay—lean on loved ones or support groups. Stay attentive to your body’s signals and don’t push beyond your limits. To guide your self-care, consider this table:
| Rest Strategies | Self-Care Practices | Nutritional Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Nap when needed | Practice mindfulness | Hydrate frequently |
| Limit screen time | Gentle stretching | Eat balanced meals |
| Prioritize sleep | Accept support | Incorporate iron-rich foods |
| Create a calming routine | Practice deep breathing | Include fiber-rich snacks |
Taking these steps promotes healing and helps you feel more grounded during this transformative time.
The Impact of Social Support on Maternal Well-Being

Have you ever wondered how social support influences a new mother’s mental and emotional health? It plays a crucial role in helping you navigate the challenges of the fourth trimester. Feeling supported reduces stress, prevents postpartum depression, and boosts your confidence. When friends, family, or partners offer reassurance, you’re more likely to feel capable and resilient. Social support also encourages better sleep and helps you focus on bonding with your baby. To deepen your understanding, consider these aspects:
Support from loved ones eases stress and builds confidence during postpartum recovery.
- Emotional validation during tough days
- Practical help with daily tasks
- Encouragement to prioritize self-care
- Sharing experiences to reduce feelings of isolation
- Access to professional resources and guidance
Feeling connected can be a game-changer for your well-being.
Navigating Family Dynamics and Expectations Post-Birth

Adjusting to family dynamics and expectations after your baby’s arrival can be challenging, especially when others’ opinions and traditions come into play. You might feel pulled between honoring family customs and trusting your instincts as a new parent. Clear communication is key—set boundaries gently but firmly, and share what feels right for you and your baby. Remember, you’re the expert on your child’s needs, not everyone else. It’s okay to politely decline advice or visits that don’t align with your comfort level. Seek support from partners or friends who respect your choices. Balancing family expectations with your well-being helps you build confidence in your parenting journey, ensuring you and your baby feel supported and secure during this transformative time.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does the Typical Fourth Trimester Last Globally?
You’re wondering how long the typical fourth trimester lasts worldwide. Generally, it spans about 12 weeks or three months after birth, but this can vary based on cultural practices and medical guidelines. In some cultures, the focus on postpartum care extends even longer. You should consider individual health needs and local customs, which influence how long this period of recovery and adjustment lasts for new parents and their babies.
Are There Specific Cultural Rituals Associated With Postpartum Care?
Think of postpartum care as a delicate dance, unique in every culture. You might find rituals like China’s “Zuo Yue Zi” or India’s “Godh Bharai,” each emphasizing rest, nourishment, and bonding. These traditions serve as guiding stars, helping new mothers navigate recovery and bonding. Embracing these rituals can reinforce your connection with your cultural roots and guarantee you’re supported during this transformative time.
How Can Partners Best Support New Mothers During This Period?
You can support new mothers by offering practical help like cooking, cleaning, and caring for the baby, so she can rest. Listen actively and provide emotional reassurance, acknowledging her feelings. Encourage her to take breaks and prioritize self-care. Be patient and understanding as she navigates recovery and new motherhood. Your support boosts her confidence and helps her feel loved, making this challenging period more manageable.
What Are the Signs of Postpartum Depression to Watch For?
Imagine your new mom friend is suddenly a moody storm cloud, unpredictable and brewing trouble. Signs of postpartum depression include intense sadness, hopelessness, irritability, trouble bonding with the baby, and changes in appetite or sleep. If you notice her withdrawing or feeling overwhelmed, gently encourage her to seek help. Your support and understanding can be the sunshine she needs to weather this storm and find her way back to calmer skies.
How Do Different Cultures View Postpartum Confinement Practices?
Different cultures have unique views on postpartum confinement practices. You might find that some cultures emphasize resting and isolating the new mother, believing it helps recovery and bonding. Others encourage social support and active involvement of family members. These practices reflect cultural beliefs about health, tradition, and gender roles. By understanding these diverse perspectives, you can appreciate how cultural background influences postpartum care and supports a mother’s physical and emotional well-being.
Conclusion
Think of the fourth trimester as planting a fragile seed—you need patience, care, and support as it takes root. By understanding the physical, emotional, and cultural aspects, you can nurture your recovery and growth. Embrace the journey with kindness and support, knowing this delicate period shapes future blooms. With proper care and love, you’ll help your new family flourish, turning this initial phase into a foundation for lasting strength and happiness.